这章主要讲内容:
- SSL/TLS;
- HTTP/HTTPS;
- 空闲的连接和超时;
- 基于分隔符和长度的协议(处理粘包,半包);
- 写大型数据。
- 序列化
SSL/TLS
安全协议:SSL/TLS
用例: HTTPS, SMTPS
实现: jdk实现(javax.net.ssl), openssl(性能更好)
Netty中的支持:
SslHandler
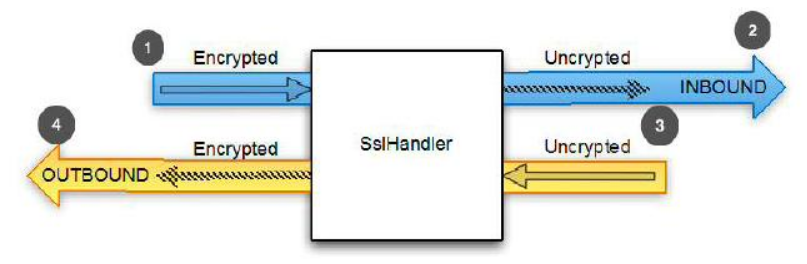
SslHandler的声明:
1
2
3
4
| -- SslHandler:
public class SslHandler extends ByteToMessageDecoder implements ChannelOutboundHandler
-- 其中的ByteToMessageDecoder:
public abstract class ByteToMessageDecoder extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter
|
由声明看出,它是一个编解码器(入站事件和出站事件都处理)。
入站: 字节=>消息(解密)
出站: 消息=>字节(加密)
具体使用则和以前的编解码器都不同:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class SslChannelInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
private final SslContext context;
private final boolean startTls;
public SslChannelInitializer(SslContext context,boolean startTls){
this.context = context;
this.startTls = startTls;
}
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
SSLEngine engine = context.newEngine(ch.alloc());
ch.pipeline().addFirst("ssl"
, new SslHandler(engine, startTls));
}
}
|
总结:
需要借用: SslContext
两个要注意的点:
- 对于每个
SslHandler 实例,都使用 Channel 的 ByteBufAllocator 从 SslContext 获取一个新的 SSLEngine(ch.alloc());
startTls: 如果设置为 true,第一个写入的消息将不会被加密;(客户端应该设置为 true)- https://github.com/devsunny/netty-ssl-example/blob/master/src/main/java/com/asksunny/ssl/StreamReader.java
HTTP相关的handler
4个解码器、编码器:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public class HttpPipelineInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
private final boolean client;
public HttpPipelineInitializer(boolean client) {
this.client = client;
}
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
if (client) {
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new HttpResponseDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new HttpRequestEncoder());
} else {
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new HttpRequestDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new HttpResponseEncoder());
}
}
}
|
消息聚合:
这回是编解码器Codec:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public class HttpAggregatorInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
private final boolean client;
public HttpAggregatorInitializer(boolean client) {
this.client = client;
}
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
if (client) {
pipeline.addLast("codec", new HttpClientCodec());
} else {
pipeline.addLast("codec", new HttpServerCodec());
}
pipeline.addLast("aggegator", new HttpObjectAggregator(512 * 1024));
}
}
|
HTTP 压缩
客户端加解压器,服务端加压缩器:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public class HttpAggregatorInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
private final boolean isClient;
public HttpAggregatorInitializer(boolean isClient) {
this.isClient = isClient;
}
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
if (isClient) {
pipeline.addLast("codec", new HttpClientCodec());
pipeline.addLast("decompressor",new HttpContentDecompressor());
} else {
pipeline.addLast("codec", new HttpServerCodec());
pipeline.addLast("compressor",new HttpContentCompressor());
}
}
}
|
HTTPS
http部分加上sslHandler就是https。不过本质上还是需要SslContext:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public class HttpsCodecInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
private final SslContext context;
private final boolean client;
public HttpsCodecInitializer(SslContext context, boolean client) {
this.context = context;
this.client = client;
}
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
SSLEngine engine = context.newEngine(ch.alloc());
pipeline.addFirst("ssl", new SslHandler(engine));
if (client) {
pipeline.addLast("codec", new HttpClientCodec());
} else {
pipeline.addLast("codec", new HttpServerCodec());
}
}
}
|
WebSocket
http仅让客户端向服务端请求数据,服务端无法主动推数据给客户端。一种解决方案是让客户端轮询,另一种解决方案是WebSocket。
用WebSocket的话,底层是tcp双向连接,服务端可以主动发消息给客户端。
WebSocket帧类型
三种数据帧:
1
2
3
| BinaryWebSocketFrame: 二进制;
TextWebSocketFrame: 文本;
ContunuationWebSocketFrame: 后续数据;
|
三种控制帧:
1
2
3
| PingWebSocketFrame: ping,对方会回pong;
PongWebSocketFrame: pong;
CloseWebSocketFrame: 关闭。
|
服务端示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| public class WebSocketServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(
new HttpServerCodec(),
new HttpObjectAggregator(65536),
new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/websocket"),
new TextFrameHandler(),
new BinaryFrameHandler(),
new ContinuationFrameHandler());
}
public static final class TextFrameHandler extends
SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> {
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
TextWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception {
}
}
public static final class BinaryFrameHandler extends
SimpleChannelInboundHandler<BinaryWebSocketFrame> {
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
BinaryWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception {
}
}
public static final class ContinuationFrameHandler extends
SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ContinuationWebSocketFrame> {
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
ContinuationWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception {
}
}
}
|
空闲事件、超时事件
WebSocket协议中多了几种事件:
| 触发时机 |
事件 |
处理方法 |
预置handler |
| 空闲时间超过配置 |
IdleStateEvent |
userEventTriggered() |
IdleStateHandler |
| 指定时间间隔内没有收到入站数据 |
ReadTimeoutException |
exceptionCaught() |
ReadTimeoutHandler |
| 指定时间间隔内没有出站数据 |
WriteTimeoutException |
exceptionCaught() |
WriteTimeoutHandler |
具体使用方法:
- 注册预置的handler,截获对应的事件;(
IdleStateHandler,ReadTimeoutHandler,WriteTimeoutHandler)
- 实现一个自定义handler注册到pipeline,处理对应的事件。
空闲事件示例:
- 注册
IdleStateHandler,负责截获空闲事件,它会调用fireUserEventTriggered方法,触发userEvent事件;
- 实现自定义
handler,处理userEvent:一种可能的处理逻辑是进行心跳检测,检测到是空闲事件就发送心跳,发送失败就关闭连接; 如果不是空闲事件,则抛出去,让下一级处理。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| public class IdleStateHandlerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel>
{
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(
new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
pipeline.addLast(new HeartbeatHandler());
}
public static final class HeartbeatHandler
extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private static final ByteBuf HEARTBEAT_SEQUENCE =
Unpooled.unreleasableBuffer(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(
"HEARTBEAT", CharsetUtil.ISO_8859_1));
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
Object evt) throws Exception {
if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(HEARTBEAT_SEQUENCE.duplicate())
.addListener(
ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
} else {
super.userEventTriggered(ctx, evt);
}
}
}
}
|
工具:解决粘包和半包(数据帧的划分问题)
netty主要是字节流层传输,并不关心应用层对数据的划分(并不关心帧是如何划分的)。
但是netty提供了很多帮助分隔帧的工具类,来解决粘包和半包的问题。
数据帧的划分问题一般有三种解决方案:
- 定长帧;
- 指定分隔符;
- head-body结构,header中规定body长度。(
HTTP)比较灵活,比较常见。
指定分隔符
相关工具类: DelimitedBasedFrameDecoder,LineBasedFrameDecoder
定长帧
相关工具类: FixedLengthFrameDecoder
head-body结构
相关工具类: LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder
高级特性: 写大文件(或大数据)
两种实现:
- 直接写文件:
FileRegion;
- 借助预置实现:
ChunkedWriteHandler。
FileReion
直接在channel中写入FileRegion即可:(还可以用ChannelProgressivePromise来获取传输进度)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
FileRegion region = new DefaultFileRegion(
in.getChannel(), 0, file.length());
channel.writeAndFlush(region).addListener(
new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future)
throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
}
}
});
|
ChunkedWriterHandler
数据流是:
数据源=>ChunkedInput=>自定义的StreamHandler=>ChunkedWriteHandler=>出站
其中ChunkedInput有4种实现:
| 实现名称 |
数据源 |
备注 |
| ChunkedFile |
文件 |
当平台不支持零拷贝,或需要转换数据时使用 |
| ChunkedNioFile |
文件 |
使用FileChannel |
| ChunkedStream |
InputStream |
|
| ChunkedNioStream |
ReadableByteChannel |
|
示例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| @Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new SslHandler(sslCtx.newEngine(ch.alloc())));
pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());
pipeline.addLast(new WriteStreamHandler());
}
public final class WriteStreamHandler
extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx)
throws Exception {
super.channelActive(ctx);
ctx.writeAndFlush(
new ChunkedStream(new FileInputStream(file)));
}
}
|
序列化数据
这里介绍3种方法:
- JDK的
ObjectOutputStream;
- JBoss marshalling;
- Protocol buffers.
JDK序列化
只要实现了Serializable接口的对象,就可以使用ObjectOutputStream。
示例代码:1
2
3
4
| FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("t.tmp");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(new Date());
oos.close();
|
Netty提供的速度优化:
ObjectInputStream =>ObjectDecoder
ObjectOutputStream=>ObjectEncoder
JBoss Marshalling序列化
比JDK序列化快3倍。
MarshallingDecoder
MarshallingEncoder
示例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| public class MarshallingInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
private final MarshallerProvider marshallerProvider;
private final UnmarshallerProvider unmarshallerProvider;
public MarshallingInitializer(
UnmarshallerProvider unmarshallerProvider,
MarshallerProvider marshallerProvider) {
this.marshallerProvider = marshallerProvider;
this.unmarshallerProvider = unmarshallerProvider;
}
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new MarshallingDecoder(unmarshallerProvider));
pipeline.addLast(new MarshallingEncoder(marshallerProvider));
pipeline.addLast(new ObjectHandler());
}
public static final class ObjectHandler
extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<Serializable> {
@Override
public void channelRead0(
ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext,
Serializable serializable) throws Exception {
}
}
}
|
其中provider的创建代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public static MarshallingDecoder buildMarshallingDecoder() {
final MarshallerFactory marshallerFactory = Marshalling.getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial");
final MarshallingConfiguration configuration = new MarshallingConfiguration();
configuration.setVersion(5);
UnmarshallerProvider provider = new DefaultUnmarshallerProvider(marshallerFactory, configuration);
MarshallingDecoder decoder = new MarshallingDecoder(provider, 1024);
return decoder;
}
|
Protocol Buffer序列化
google的序列化方案。
主要是4个类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder: bytes=>msg; 解析出头部的长度字段,以正确划分帧;
ProtobufDecoder: msg=>msg;
ProtobufVarint32LengthFieldPrepender: msg=>bytes; 头部添加长度字段.
ProtobufEncoder: msg=>msg.
|
示例代码:
服务端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(new ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder())
.addLast(new ProtobufDecoder(
ProtoObject.Req.getDefaultInstance()))
.addLast(new ProtobufVarint32LengthFieldPrepender())
.addLast(new ProtobufEncoder())
.addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
})
|
客户端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(new ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder())
.addLast(new ProtobufDecoder(
ProtoObject.Resp.getDefaultInstance()))
.addLast(new ProtobufVarint32LengthFieldPrepender())
.addLast(new ProtobufEncoder())
.addLast(new ClientHandler());
}
})
|
ProtobufDecoder实际上可以接受MessageLite或者Builder。
Message是MessageLite的子接口,因此可以用Message代替MessageLite。(基类指针存放子类对象)
1
| public interface Message extends MessageLite, MessageOrBuilder {...}
|

